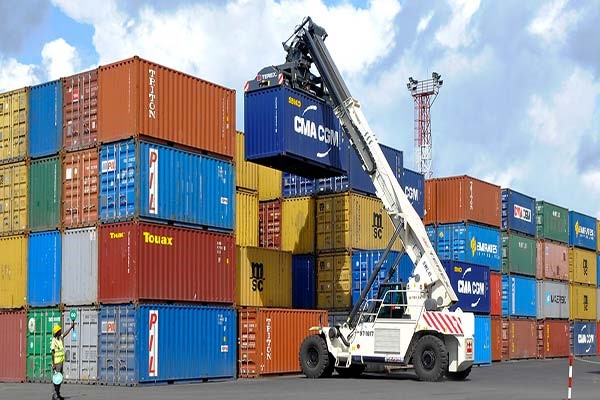
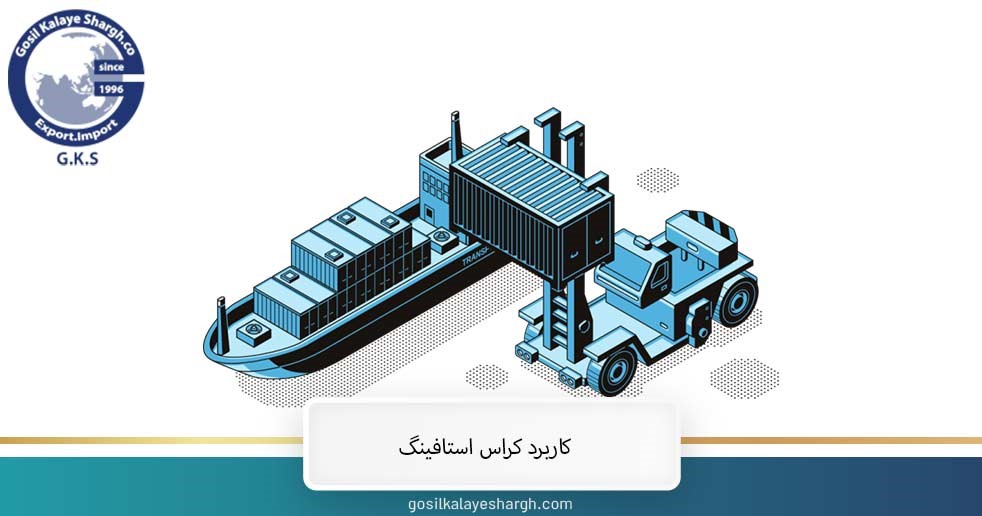
Cross-stuffing is the most important method of moving goods, in which the cargo is unloaded from one container and enters another container. By using this technique, the transfer speed is increased and the cargoes are transferred completely safely. We will discuss this issue further.
Application of cross-staffing
Cross-staffing is widely used in sea transportation and can be used to move different goods. This well-known method is available to transport companies with the following applications:
- Division of large shipments
The first application of cross-staffing is to divide large goods into small ones. When there is not enough space to unload and receive cargo at the destination port. The cargo is divided into small parts and placed on small ships.
- Lack of direct communication path
If there is no direct route from the port of origin to the destination, cross-staffing makes it possible for shipping companies to deliver the cargo to the destination through the transit of the third port.
- Sanctions in the destination country
Other uses of cross-staffing include sending cargo to embargoed countries. If a country is politically and economically embargoed, goods can be transferred to it only with this method.
This method is used in international transportation industries, industries requiring customs clearance, and marginal industries, and it brings many advantages.
Cross-staffing process
Cross-staffing is a special process that is implemented in some ports today. In this method, companies need to use a third port to transfer cargo. This method is often carried out in the port of Jebel Ali located in the United Arab Emirates. Companies that intend to use this practical technique must first issue their bill of lading, certificate of origin, invoice, packing list and other documents to the trading company.
The original documents and bill of lading must be delivered to Shore before the cargo arrives so that the relevant carrier can be received. When the goods enter the customs, customs formalities and cross-staffing operations are performed on them first, and then the cargo is cleared by the company and sent to the final destination.
You have only one to two days to perform this operation. Jabal Ali port is the place of unloading and loading of cargoes that cannot directly enter some countries, including Iran. In the export of nylon to Iran, sea transportation companies need to use this method.
What products need cross-staffing?
Cross-staffing is needed for goods that do not have the conditions to enter some countries due to embargo and cannot be imported directly into the country. When the shipping company cannot serve some countries through shipping lines in ports, it uses this method. Products that require cross-staffing include:
- Car spare parts
These parts are among the goods that need the cross-stuffing method for transportation. The embargo of some countries has made them unable to use foreign parts directly. In importing Renault truck and its parts, it is necessary to get help from a third country.
- Electronic appliances
Electronic devices such as professional cameras, laptops, mobile phones and advanced systems are among the devices that are prohibited to be sent directly to the embargoed countries. You must use the cross stuffing method to send these devices.
- Household appliances
To send some household appliances such as TV, refrigerator and washing machine and dishwasher to the embargoed countries, you need to use the cross-stuffing method. With this, you can get the supplies with the help of a third country.
- Food and cosmetic products
Due to the embargo, some food and cosmetic products cannot be directly imported into some countries such as Iran. But with the staffing method, you can get help from a third country and import these items indirectly.
Various factors such as sanctions, restrictions and new laws play a role in sending this cargo and using the staffing method, and each product has its own rules.
Disadvantages of cross stuffing
In addition to its advantages, the cross-staffing method also has disadvantages that we present here:
- This method is done indirectly and has its own problems.
- Ships used in cross-staffing require special equipment such as cranes, which are expensive to procure.
- Using staffing to bypass sanctions can cause cargo to stop and heavy damages.
- Due to the increase in transportation costs in this method, you will see an increase in the price of imported goods.
- If the cargo transfer is not done correctly, the cargo will be damaged.
The cost of cross-staffing
The cost of cross-staffing depends on various factors, such as the nature of the product, the type of packaging, the need for transportation equipment, and the method of handling. This cost includes the cost of unloading cargo from containers and reloading, the cost of international transportation and import and export. The higher the load, the higher the rate. Important and security shipments, which have a lot of value, are generally moved at a higher cost.
Cross-staffing requires more money than other methods. If the cargo needs special equipment for handling, the company must pay more. On average, the cost of cross-stuffing for each container with a size of about 20 feet is about 300 to 400 dollars, and if the amount of cargo is added, this cost will increase.
The importance of the cross-staff method for Iran
The cross-staffing method is very important for Iran; Because he can have access to the goods he needs even in the conditions of embargo. The political and economic embargo has made Iran unable to directly import goods. For this reason, the companies get help from the third country to indirectly import the required goods into the country.
Iran’s good geographical position has made it possible to avoid sanctions in several ways. To do this, the companies first load the ship in the port of Iran and deliver it to other countries through a third country. Cross-staffing has been able to help a lot in the field of exporting and importing goods to Iran.
Does the cargo get damaged in cross stuffing?
In the cross-staffing operation, it is very important to preserve the health of the goods; Because a small damage can cause heavy damages. This work requires sufficient expertise and experience and should be sent by reputable companies such as If the handling of cargo from containers is not done correctly and carefully, there is a possibility of damage. To use this method optimally, you must make the necessary arrangements and proceed with detailed planning. The health of the goods and not seeing them damaged can increase the credibility and popularity of the transport company.
The difference between cross-staffing and transshipment
Cross-staffing has many differences with transshipment. At the crossing, the cargo is unloaded from the container and enters the ship’s container; But in transit, the container is sealed from one ship to another. In this process, there is no need to unload and reload, and this can reduce the cost to some extent.
In cross transportation, cargo arrangement is done directly without changing the route, that is why it is used in sea, land, air and rail transportation industries. In transshipment, a person or a company sends its ship or plane Another company rents to do the transportation.
final word
Cross-Staffing is a safe and widely used way to export and import goods and embargoed countries can easily use it. This method is done at a higher cost and is the best option for goods that are embargoed.
With advanced equipment and a brilliant history, Gasil Company has been able to provide the best services in cross-staffing. You can consult experts before starting work. This work requires expertise and skill and our team can do it in the best way.